In this article
Taking exogenous growth hormone is the only effective way to manage the debilitating symptoms of growth hormone deficiency (GHD).
The serum GH levels will rise as soon as the first injection, but it will take at least a month until you start noticing the benefits of the therapy.
One of the first results you will experience is a reduction in belly fat and a slimmer waistline. Patients also report improved energy levels, increased lean mass, and higher bone density. Usually, all symptoms of GHD disappear within the first year of treatment.
Unfortunately, discontinuing the medications will cause your GH levels to return to pre-treatment levels, and your symptoms will likely follow.
Currently, there is no consensus on how long HGH therapy should last. Therefore, you should always consult with an experienced endocrinologist who will best determine the course of your treatment and how long you should stay on HGH therapy.
What is the half-life of HGH?
Injecting HGH under the layers of the skin (subcutaneously) is the preferred method for administering growth hormone when compared to intramuscular and intravenous injections.
That’s because subcutaneous injections prolong the growth hormone’s plasma (circulating) half-life and allow for a single injection a day. Trials reveal that the plasma half-life of subcutaneous HGH injections is 7-10 hours.
In comparison, the plasma half-life of the naturally produced GH in your body (or injected intravenously) is only 20 minutes. Therefore, subcutaneous injections help mimic the natural release of GH by the pituitary gland, which happens on several pulses, mainly throughout the night.
How long does HGH take to work?
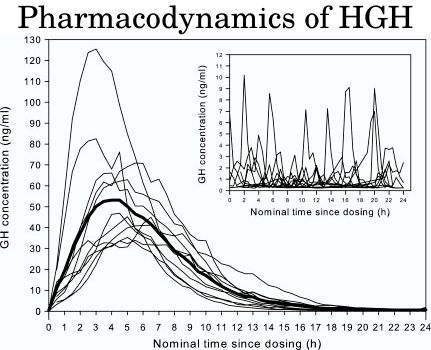
Your serum growth hormone levels will start rising within minutes after subcutaneous injection, but the increase will gradually reach a peak 4 hours after the injection. Furthermore, it will take 11-12 hours in total after the injection until your plasma GH levels reach baseline values.
HGH works by binding directly to the growth hormone receptors, which can be found in various tissues. The hormone triggers the synthesis of IGF-1, which stimulates cellular and tissue growth.
This is why HGH therapy helps increase lean body mass, bone mineral density, skin collagen, and hyaluronic acid levels, etc. Furthermore, HGH directly stimulates enzymes in adipose tissue that leads to the release of fat and the shrinking of fat cells.
Growth hormone also helps increase energy levels, boost mood and improve sleep. The benefits of the treatment usually become noticeable 1-2 months after the start of the therapy. Your body will benefit from HGH injections for as long as the therapy lasts, and there is no risk for developing a “tolerance”.
The risk of HGH side effects depends on the dose. The most common side effects include symptoms of water retention such as carpal tunnel syndrome, achy joints, and edemas.
These adverse reactions last only for a few weeks or until your body adapts to the new GH levels. In fact, they can be avoided completely by gradually increasing the dose.
Growth hormone has anti-insulin effects, so HGH therapy increases insulin resistance. These effects are also not permanent, and research suggests that insulin resistance usually goes back to normal within 3 months of therapy.
How long does HGH stay in your system?
If you have taken an injection, HGH will remain in your system for up to 48 hours until it is completely broken into different by-products. There are 2 main tests that can detect the use of exogenous growth hormone – the isoform test and the biomarkers test.
GH isoform test
The isoform test can detect the use of HGH within the first 48 hours and works by comparing the ratios of the different forms of the hormone in your body.
HGH injections contain growth hormone that is identical to the main type of HGH produced in humans, so a simple test of serum growth hormone levels won’t be effective.
Yet, this is not the only type of growth hormone which your body produces. There are other forms produced in the human organism, and your body maintains a balance between the different types.
That’s why the isoform test uses the ratio between the other types of growth hormone produced by your body and the one that can be both produced endogenously or injected. Changes in that ratio cannot occur naturally and indicate the use of exogenous HGH.
HGH Biomarkers Test
The biomarkers test can detect by-products of HGH, which occur at least 48 hours after injection. Thus, the test is effective in detecting exogenous growth hormone from 48 hours to 3 weeks after injection.
Despite the fact that some amounts of the medication remain in your body for up to 48 hours, GH levels usually return to pretreatment levels within 12 hours of the injections.
There are no medications that may interact with the metabolism of HGH or speed up its elimination. On the other hand, HGH may increase the activity of liver enzymes and speed up the metabolism of all medications metabolized by the cytochrome P450 family of enzymes.
On the other hand, it takes much longer for IGF-1 levels to drop since its half-life is 20-30 hours. Thus it may take up to a week before IGF-1 levels drop after discontinuing HGH therapy.
What happens when you stop taking HGH?
HGH therapy can be discontinued at any time, but doing so will likely cause your symptoms to reappear.
Adolescents and young adults who discontinue growth hormone therapy experience a decrease in their metabolic rate as soon as 2 weeks after discontinuation.
However, it takes several months until symptoms reappear. The first symptom to reappear is fat gain, more specifically, increased adiposity around the waist. Due to the growth hormone effect on metabolism, adolescents gained 4.3% of body fat on average in a year.
Children who haven’t reached a final height and stopped taking HGH therapy may also experience an increase in body fat. Unfortunately, their linear growth will stall, and they may not reach a normal adult height unless they resume therapy before the end of puberty.
Another study in adults reports that discontinuation for longer than 3 years also leads to unfavorable changes in bone mineral density and blood cholesterol levels. Furthermore, the younger adults in the study lost body mass while gaining body fat which may indicate loss of lean muscle. The benefit that lasts the longest after discontinuing HGH therapy is increased bone mineral density. Yet, no benefits are permanent.
Long-term HGH therapy will not suppress your endogenous synthesis, and your serum GH levels will return to baseline after discontinuing growth hormone treatment.
How long does HGH withdrawal last?
Research reveals that patients with severe GHD are most likely to experience withdrawal after discontinuing HGH. The symptoms of HGH withdrawal included decreased energy, and increased tiredness, pain, irritability, and depression.
These complaints occurred within the first 3 months of discontinuing HGH injection. In addition, symptoms of GHD also contribute to these and more complaints, such as weight gain, muscle loss, osteoporosis, and chronic fatigue.
It is difficult to estimate how long the symptoms of withdrawal last since they overlap with the signs of severe GHD. Lack of growth hormone can also lead to severe fatigue, depression, and cognitive problems.
Decreasing the dose of HGH more slowly rather than quitting it cold turkey may cause the symptoms of GHD to appear more gradually. But the only way to prevent any symptoms of GHD from reappearing is to continue taking HGH injections under medical supervision.