In this article
Your body preserves its youthfulness and vitality by producing a growth hormone.
Unfortunately, its levels start to decrease after you turn 30 and then plummet with the onset of menopause. That’s because your growth hormone (HGH) levels are tightly related to your estrogen status and overall hormonal balance.
The role of balanced GH levels in women is crucial. If you already have any of the signs and symptoms we have listed below. You should visit an experienced physician who will diagnose you and determine whether you are eligible for HGH therapy.
What does growth hormone do for females?
HGH also called somatotropin, is well-known as the main stimulus for growth in children. It is produced by the pituitary gland in the brain.
But the role of the growth hormone in adults is not any less significant. The secretion of GH normally continues in adult life and the hormone regulates fat and muscle metabolism, cell growth, and tissue regeneration in both men and women.
HGH has a well-established role in skin health and renewal
Growth hormone is often associated with muscle-building effects in males but in reality, women have significantly higher physiological levels. Its secretion has a pulsatile fashion with multiple daily peaks. They are higher and more frequent in women than men.
HGH levels in females may reach up to 14 ng/mL (630 pmol/L) during a peak
Skin is one of the tissues with a significant capacity for regeneration and according to studies, there are skin receptors for HGH, which is required to stimulate the process. Researchers report that HGH is required for the development and maintenance of normal bone mineral density as well.
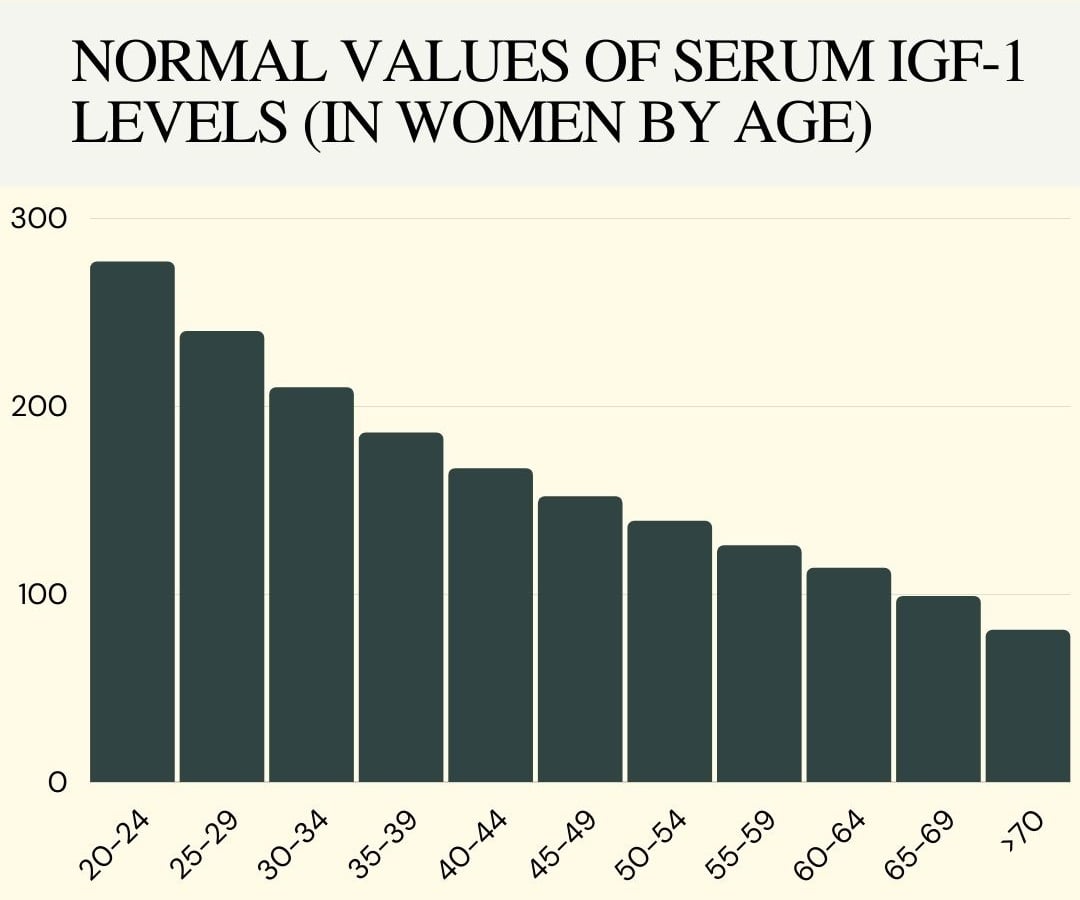
Most of the effects of growth hormone are mediated by another hormone called insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). HGH stimulates its production by the liver but IGF-1 does not have the same pulsatile secretion. Instead, it reflects the mean GH levels. The normal range of IGF-1 in women by age has been reliably estimated by scientific studies:
age 20–24 ≥ 200.6 – 370.6 ng/mL
age 25–29 ≥ 171.4 – 324.6 ng/mL
age 30-34 ≥ 148.6 – 286.3ng/mL
age 35-39 ≥ 130.8 – 255.0ng/mL
age 40-44 ≥ 116.7 – 229.6 ng/mL
age 45-49 ≥ 105.2 – 209.0 ng/mL
age 50-54 ≥ 95.1 – 191.5 ng/mL
age 55-59 ≥ 85.6 – 175.5 ng/mL
age 60-64 ≥ 75.7 – 159.3 ng/mL
age 65-69 ≥ 64.5 – 140.9 ng/mL
age over 70 ≥ 51.5 – 118.2ng/mL
Growth hormone deficiency in women
Normally, females have higher levels of growth hormone than men because they have significantly more estrogen. According to scientists, estrogen has a direct stimulating effect on GH secretion.
Studies also suggest that estrogen inhibits the liver production of IGF-1. This is feedback for the pituitary gland to secrete more HGH in order to maintain normal IGF-1 levels.
When a woman enters menopause, estrogen levels plummet and this lowers HGH levels significantly, without affecting IGF-1. Low GH levels no longer have the same direct stimulus for burning fat tissue which may result in gaining weight around the waist and visceral obesity.
Studies report that weight gain in women coupled with menopause can lead to a significantly elevated risk of heart problems
The symptoms of menopause can be similar to those experienced due to low HGH:
- Weight gain
- Trouble sleeping
- Lack of sex drive
- Decreased bone density
- Depression and mood swings
Menopausal women who are already on hormone replacement therapy with estrogen might also need higher doses of HGH. Studies show that despite the stimulating effect of estrogen, it doesn’t lead to higher or longer peaks of GH.
Furthermore, it has a suppressing effect on IGF-1 production, so a higher dose of growth hormone might be required in order to achieve normal IGF-1 levels during growth hormone therapy.
Adult-onset GHD has an impact on mood and mental well-being as well. Depression and even social isolation are some of the most common symptoms reported by those suffering from low HGH. Other symptoms may include a lack of libido, chronic fatigue, and low bone density.
In order to get diagnosed correctly, you should be medically examined and tested by a specialist. Performing a simple blood test can’t provide reliable information for diagnosing GHD because of the pulsatile secretion of the growth hormone. This is why all eligible patients are assigned to a growth hormone stimulation test.
It involves the stimulation of an HGH peak with the help of pharmaceuticals. The test has to be performed in a controlled medical environment by an experienced physician who has evaluated the possible risks and contraindications.
The cases of GH deficiency in adult women can be either acquired or idiopathic. Idiopathic GHD rarely occurs during adulthood and the cause cannot be determined by modern medicine. It is much more common for this type of GHD to first occur during childhood and then continue into adulthood.
The majority of adult-onset GHD cases are acquired, meaning there is a cause that can be identified. The most common causes include:
- Tumors
- Brain surgery
- Ionizing radiation
- Severe head trauma
- Infections of the brain
- Infarction of the pituitary gland
HGH replacement therapy for women
The most effective way to treat the symptoms of GHD is the administration of exogenous growth hormone as a prescription medication. The daily administration of this hormone is called HGH therapy.
GH used for the therapy is produced by a recombinant DNA technology that creates a bioidentical hormone to the one naturally produced in the human body.

The only form of HGH therapy approved by the FDA is growth hormone injections as they are the only reliable route for administering growth hormones into the human body. That is because of the specific structure of the hormone. GH is a peptide hormone that can be easily inactivated by your digestive system and it can’t get effectively absorbed by your skin or mucous membranes.
In other words, HGH injections are the only form of growth hormone replacement therapy that works as other methods are not successful in delivering the hormone inside your organism.
Any products marketed as HGH gels or pills and sold without a prescription are a scam
Benefits of HGH therapy for women
HGH therapy for women can provide a wide range of benefits:
- Losing fat around the waist and internal organs
- Less depressive symptoms and better mood
- Improved skin repair and regeneration
- Improved cholesterol levels
- Increased bone density
- Improved quality of life
- Improved hair growth
- Increased sex drive
Especially during menopause, long-term HGH therapy may significantly reduce the risk for osteoporosis, according to trials that lasted for up to 2 years. If bone loss is left untreated, it might be initially asymptomatic until eventually accidental fractures or collapsed vertebrae occur.
In such cases, a combination of HGH therapy and estrogen replacement therapy might be required.
GHD combined with menopause can lead to hot flashes, night sweats, and restlessness that may negatively impact your sleep and overall quality of life. Researchers suggest that HGH therapy can reverse sleep disturbances by preventing overactivity of the hypothalamus.
Most of the HGH benefits in women occur during the first six months of therapy
Here is a short timeline of HGH benefits you can expect:
- 1st month – a peak in IGF-1 levels. Most of the benefits are still on cellular levels, including improved cell and tissue regeneration.
- 2nd month – improvement in hair growth and skin complexion. Fat deposits around the waist may start to decrease.
- 3rd month – noticeable reduction in belly fat. This results in an improved lipid profile and metabolic health. Increased energy levels and better sleep.
- 4th – 6th month – reduction in symptoms of depression. Improved mood and quality of life. Further improvements in body composition.
Side effects of HGH for women
Initially, HGH therapy is often prescribed in doses as low as 0.2 mg per day and then is slowly increased under medical supervision. Careful control over the dosage eliminates the risk of side effects. Higher doses can lead to water retention and temporary adverse reactions such as:
- Joint and muscle pain or discomfort
- Swelling of hands and feet
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Headache
All of these side effects are transient and relieved when the dosage is reduced or the therapy is discontinued.
Nevertheless, if you experience any adverse reactions you should first consult with your physician, instead of changing the dose on your own
Your doctor will help you with the proper adjustment of your HGH therapy in order to avoid side effects while still addressing your GHD symptoms successfully.
However, the use of illegal HGH supplements by females who are aiming for anti-aging and rejuvenation might hide additional risks.
HGH products sold without a prescription are often counterfeit and their ingredients remain unknown. Using such substances might lead to unexpected side effects and health problems. Allergic reactions to some of the non-labeled ingredients are also possible.
High doses of growth hormone can lead to transient insulin resistance. This has led to the misconception that HGH therapy might increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. However, large studies have revealed that there is no evidence for a higher incidence of type 2 diabetes amongst people on legal therapy.
Another common misconception is that HGH might increase the risk of cancers but once again, trials with thousands of patients do not report a higher incidence of malignancies.
HGH Therapy For Men

HGH therapy for men can lead to improvements in Body Composition, Sexual Function, Energy, Mental Health
Women have higher concentrations of growth hormone in the blood which are tightly related to their estrogen levels. When the estrogen decreases during menopause, growth hormone levels plummet as well.
HGH therapy in women can lead to abdominal fat reduction, better skin and hair, improved mood, and increased energy levels. Furthermore, body composition changes can reduce the risks of atherosclerosis, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.